Jun 13, 2023
How Long Do Bear Markets Last?

The duration of bear markets can vary, but on average, they last approximately 289 days, equivalent to around nine and a half months. It’s important to note that there’s no way to predict the timing of a bear market with complete certainty, and history shows that the average bear market length can vary significantly. For example, the bear market spanning 1973–74 lasted a whopping 630 days, whereas the bear market in Q1 of 2020 lasted a relatively short duration of just 33 days.
The recent bear market has finally come to an end after a grueling one-year journey. This duration surpasses the average length of bear markets, which typically span around 9.6 months. Although it was a challenging period for investors, it is important to note that this one-year duration falls short of the record-breaking bear market of 1973/74, which persisted for a staggering 20 months. While investors may have endured a longer downturn than usual, the comparison to the longest-ever bear market serves as a reminder that market cycles can vary significantly in duration.
A bear market indicates a steep decline in stock prices. While bear markets can represent nothing more than normal stock market fluctuations, they can also be a signal of a more serious downturn—or an impending recession.
Bear markets are nothing new, and we’ve had many in the past. However, the most recent bear market has garnered attention amid rising inflation, interest rate hikes, and other economic factors.
This leads to some logical questions: what is a bear market? How long do bear markets last? What comes after a bear market?
Here’s what to know about bear markets, how long they last, and what it all means for your investments.
What is a bear market?

A bear market is when a stock market index declines in value by at least 20% following a recent high. Often accompanied by negative investor sentiments, it’s an easy way for Wall Street to mark that stocks have taken a tumble, indicating a sustained market downturn.
The opposite of a bear market is a bull market, when the value of a stock market index rises 20% or more. Bull markets indicate that the economy is strong, stock prices are trending upward, and investors are confident.
If there’s one thing to know about bear markets as a new investor, it’s that they’re normal. The S&P 500 has weathered 29 bear markets since 1928, with stock values decreasing by 36% on average each time. However, there have also been 27 bull markets—typically following the end of a bear market—with stock values increasing by 114% on average.
Why does this matter for you and your money? Because it tells us that stocks have historically risen significantly over long periods of time following a bear market. This means if you can stay invested even when the market is down, it can be a huge opportunity once stocks begin to rise again—one that can move the needle on your long-term wealth goals.
Bear market history

A look at the history of bear markets can provide insight into how this most recent bear market fares in comparison. On a high level, we’ve seen fewer bear markets occur since World War II:
- There were 12 bear markets between 1928 and 1945 (pre-World War II), taking place roughly every 1.4 years.
- Since 1945, there have been 15, lasting from just a month to 1.7 years.
If we look at every bear market since World War II, data shows that it takes 12 months on average to go from “peak to trough”—the period of time between the end of market highs (peak) and when the market transitions from its decline (the bear market) to expansion. The trough phase essentially represents the market hitting rock bottom, and it can only go up from there.
That said, there’s no way to predict the timing of a bear market with 100% accuracy, and history shows that the average bear market length can vary significantly. For example, the bear market in 1973–74 lasted a whopping 630 days, while 2020’s bear market in Q1 lasted just 33 days.
How to invest in a bear market
Regardless of how long bear markets last, the good news is that investors can anticipate rising stock prices and strong returns once they end, since history shows that bear markets typically precede bull markets.
Investor Tip: The average returns following the end of a bear market are 43.4% after 12 months—meaning the best strategy for investing in a bear market is to simply stay invested. (Wells Fargo)
Of course, your bear market investing strategy will vary depending on how close you are to retirement. But for younger investors with a longer time horizon, your best option is to stay the course.
There’s no denying the discomfort of investing during a bear market, but you’re more likely to survive the downward cycle if you’re investing for the long term. The same can’t be said for short-term investors hoping to cash out for a profit during a bear market, however. Regardless of which camp you fall into, the following tips can make investing during a bear market a little easier:
- Hold enough cash: if you’re nearing retirement, having enough cash can prevent you from needing to sell stocks at a loss if you need access to funds.
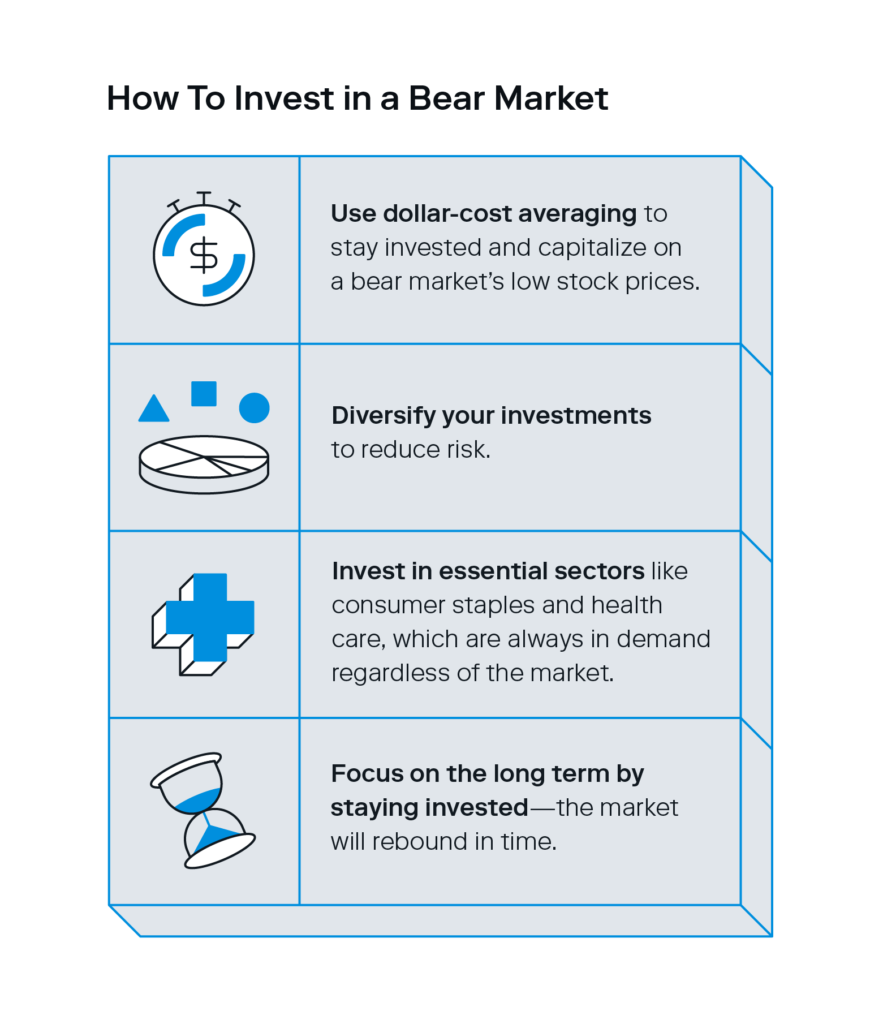
- Use dollar-cost averaging: to capitalize on a bear market’s low stock prices, this strategy of periodically investing a fixed amount of money over time (versus investing it all at once) reduces risk and allows you to stay invested in the market, regardless of how it’s performing.
- Diversify your investments: a diversified portfolio is key to weathering a bear market since holding a wide range of investment types can reduce your overall risk and provide a cushion for market volatility.
- Look at sectors that perform well during bear markets: Consumer staples, health care, and other essential sectors usually withstand bear markets since they’re always in demand. Known as defensive stocks, they make great investment opportunities during periods of downturn.
- Focus on the long term: Remember that no matter how dire the market seems, it will eventually turn around. You’ll reap more rewards by staying invested for the long haul versus panic selling when times are tough.
While the answer to “how long do bear markets last?” is difficult to predict, investors should find comfort in the fact that the S&P 500 has regained and exceeded its value following every bear market we’ve seen in the past.
Investing made easy.
Start today with any dollar amount.

Bear Market FAQs
Still have questions about bear markets? We have answers.
Do Bear Markets Indicate a Pending Recession?
While bear markets have often been associated with recessions, one doesn’t necessarily cause the other. That said, recessions have accompanied 9 of the last 17 bear markets—meaning since the 1900s, the U.S. economy has managed to avoid a recession 30% of the time following a bear market.
Looking ahead, the deeper stock prices continue to fall, and as long as the Federal Reserve continues to hike up interest rates, the higher the risk of a recession.
When Was the Last Bear Market?
Excluding the bear market that just ended June 2023, the last bear market occurred in March 2020 amid COVID-19 pandemic lockdowns that lead to a brief recession. The bear market lasted only 33 days.
Where Does the Phrase “Bear Market” Come From?
It’s likely derived from the jargon originating in the 1700s or 1800s. The term “bearskin” was commonly used in reference to selling bearskins, and etymologists often reference the proverb warning not to “sell the bear’s skin before one has caught the bear.” Eventually, bearskin was shortened to bear and was applied in reference to stock being sold.
Related Articles

The 12 Largest Cannabis Companies in 2024

Saving vs. Investing: 2 Ways to Reach Your Financial Goals

How To Invest in the S&P 500: A Beginner’s Guide for 2024

Stock Market Holidays 2024
The 2024 Financial Checklist: A Guide to a Confident New Year

How To Plan for Retirement





